~cosmos-magazine | Bookmarks (522)
-
New insights into Io, Mars announced at AGU
In a big day for planetary science, scientists have announced major news regarding the exploration of...
-
New timeline of neanderthals interbreeding with humans
Most non-African people today inherit 1-2% ancestry from Neanderthals, and researchers have long searched for clues...
-
Gene therapy shows promise for reversing heart failure
A new gene therapy may give hope to the more than 64 million people living with...
-
Women with high levels of ‘interoception’ orgasm more often
A new study investigating the female orgasm has found that women have more frequent and satisfying...
-
Giving E. coli a Superman cape to make greener medicines
We normally think of E. coli as something that makes us sick, but the bacteria also...
-
Urgent intervention needed to curb global tourism emissions
As the remaining carbon budget to limit global warming to 1.5°C dwindles – expected to run...
-
Firefly Sparkle shines light on 600 million year old universe
Astronomers have trained the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on a galaxy named “Firefly Sparkle.” But...
-
Concern for seals as icebergs melt
Climate change is putting the future of some seals at risk as icebergs on which they...
-
Humpback whale travels 1/3 around the world to breed
Animals are known to go to great lengths for the opportunity to breed. A new study...
-
Solar probe nears the Sun, as scientists report on eclipse
As the Parker Solar Probe readies to dive to the Sun on Christmas Eve, scientists at...
-
How to avoid bumpy bus rides: jerk-measuring device
A jerking, lurching bus ride can be enough to put someone off their lunch – or...
-
Zooplankton diet could have big greenhouse benefits
An American-led research team has developed a new way to sequester more carbon dioxide at the...
-
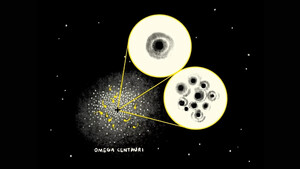
Black hole debate at centre of Omega Centauri ongoing
Astrophysicists have added further flames to a 20 year debate about what lies at the centre...
-
Study questions if women are more prone to ACL injuries?
New findings, published in respected and influential British Journal of Sports Medicine, challenge the common claim...
-
New $20 million Australian research centre to tackle responsible AI
As artificial intelligence becomes more pervasive, a new research institute in Adelaide, Australia will be looking...
-
Google’s quantum computer takes major leap forward
Researchers at Google Quantum AI have managed a new milestone in quantum computing, with chips that...
-
EV batteries: manufacturers underestimate lifetime by 38%
Electric vehicle (EV) batteries may last longer in the real world than manufacturing lab tests predict,...
-
Expert verdict on Gencost: renewables still cheaper than nuclear
Independent energy experts largely – although not universally – agree with an economic analysis that finds...
-
One mutation in H5N1 bird flu could enable human infection
A study funded by the National Institutes of Health in the US has found the H5N1...
-
What fossils can reveal about ancient Australian forests and fire
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Australia’s forest ecosystems, renowned for their extraordinary diversity of rare plants and...
-
Theoretical physicist wants to know what’s at a singularity
Over the course of her career Susan Scott has explored the fundamental question of how gravity...
-
Computer science role models dominated by 5 tech bros
A UK study confirms that secondary students lack diverse role models for computer science, likely compounding...
-
Renewables set to be cheapest Australian energy again
Renewables look likely to be the cheapest energy source in Australia again next year, according to...
-
3D scans of giant hailstones could help weather forecasting
Weather scientists have used 3D scans to delve deep into the inner anatomy of hailstones, providing...